Inertial Navigation Automatic Guided Vehicle (AGV)
Introduction
The Inertial Navigation Automatic Guided Vehicle (AGV) has advanced technology, high accuracy, high flexibility, convenient combination and compatibility, which is widely used in different areas.
Relative to the magnetic navigation AGV products, inertial navigation AGV products is one of track navigation AGV. It does not need fixed route, with greater freedom of movement, particularly suitable for intelligent mobile warehousing logistics, workshop assembly application scenarios.
The running route of the inertial navigation AGV can be dynamically generated. The users can automatically generate transportation tasks according to the requirements of software such as ERP and WMS. Or through the personnel, the station to carry on the dynamic call function, or through the automation equipment interface with PLC, CNC, elevator, according to need to complete the logistics transportation task.
Inertial navigation AGV products have more flexibility, not only can be used indoors, but also be used in outdoors, not only to adapt to the common ground, but also can adapt used in steel floors. The product form can be applied from non-standard to industrial standardized vehicles.
Intelligent electronic map, CAD, YAML map expression, Under the path, AGV is based on the board map route, and the path change is simple and convenient.
Trackless navigation technology, strong traffic control system, more flexible deployment capability. The site task changes in real time, selecting the optimal route according to the actual situation.
Multiple docking modes, latent traction, latent lifting, tail traction, load shifting, etc.
The system realizes intelligent logistics, flexible assembly and so on.
Software, hardware system performance is stable, safe, reliable, easy to maintain.
Simple construction path, no trace of the construction after the end of maintenance-free, no maintenance costs.
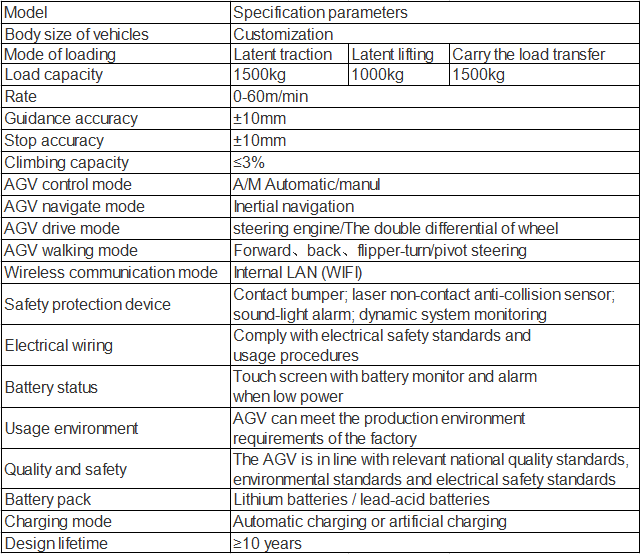
Specifications
Application Techniques
1.What is the Device Interface Definition of MEMS North Seeker
2.What Performance is the FOG sensor in FOG North Finder
3.Where are MEMS Gyroscopes Used?
4.Research Background and Current Status of MEMS IMU
5.How do parameters affect the performance of the quartz accelerometer?
6.Background and Development Status of MEMS Inertial Sensors
More Products