In recent years, the field of deformation monitoring has witnessed significant advancements, largely driven by the widespread adoption of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology. This technology, originally developed for navigation and positioning applications, has found extensive use in various fields, including geodesy, surveying, and deformation monitoring. This article explores how GNSS technology, when applied to deformation monitoring, brings about innovation and efficiency.
1.What is GNSS Monitoring?
Every time you open your phone's map navigation or hear the voice prompt "turn right in 500 meters" while driving, you may not realize that it all relies on it.
GNSS, the Global Navigation Satellite System, including Beidou and GPS, is widely used in geodesy, deformation monitoring, and other fields due to its all-weather and high-precision characteristics. GNSS monitoring technology tracks real-time deformations and displacements of large-scale engineering projects, assesses building safety and operational conditions, reduces workload, and achieves unmanned operations.
Deformation monitoring refers to the continuous observation and analysis of changes in the shape, position, or size of objects or surfaces over time. It plays a crucial role in various engineering and geoscience applications, such as monitoring the stability of structures, assessing geological hazards, and studying tectonic movements.
Based on this technology, deformation monitoring GNSS receivers designed for complex environmental monitoring integrate Beidou/GNSS technology, with characteristics such as high adaptability, stability, easy deployment, easy maintenance, and low power consumption.
One of the key advantages of GNSS technology in deformation monitoring is its ability to provide accurate and precise positioning data in real-time. GNSS receivers, equipped with multiple satellite antennas, can track signals from a constellation of satellites orbiting the Earth. By processing these signals, GNSS receivers can determine the receiver's position with high accuracy, typically within a few centimeters.
2.GNSS Empowers Precise Deformation Monitoring Technology
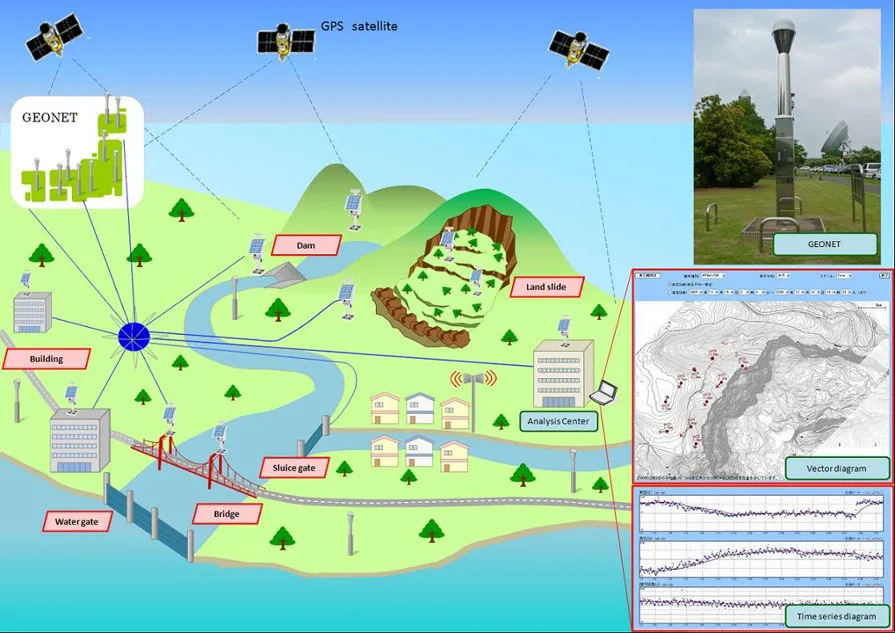
Deformation monitoring involves continuous observation and analysis of changes in object shape. To accurately predict deformation trends, a real-time, high-precision monitoring system is required, and GNSS technology meets this demand. The monitoring principle of this system is to automatically monitor surface displacements of dams using GNSS, receiving GPS signals in real-time and transmitting them to the control center. Server software processes the data, determining the three-dimensional coordinate changes of each monitoring point and issuing alarms based on preset warning values.
3.Cloud Empowerment: Achieving Efficient Deformation Monitoring Platforms
The deformation monitoring GNSS cloud monitoring platform integrates the Global Navigation Satellite System and cloud computing technology, providing real-time monitoring and data analysis services. GNSS receivers deployed on targets acquire accurate position and time data, which are processed and analyzed by cloud servers. The platform boasts high data stability, compatibility with various sensors, strengthened communication stability, and millimeter-level perception of subtle changes.
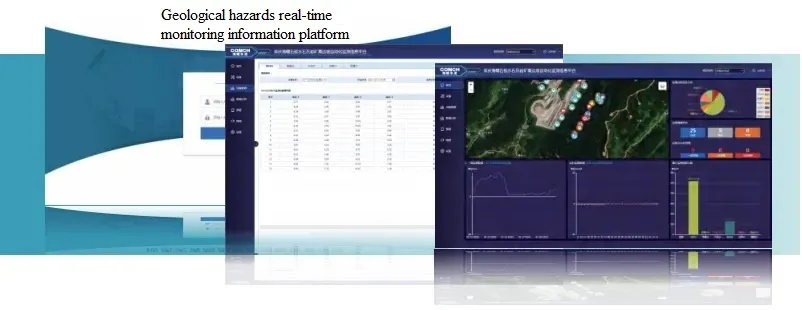
Its visualization monitoring function provides clear information on monitoring points and overall situations. Cloud access is convenient without requiring software installation, thereby enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, the platform supports various warning modes, offering comprehensive online monitoring and alert services.
4.Exploring the Superior Performance of GNSS in Deformation Monitoring
- High Integration: Integrates GNSS, sensors, and other functions into one unit, making installation and maintenance simple.
- Ultra-Low Power Consumption: Continuous operation consumes less than 1.5W, reducing the need for solar power supply and saving costs.
- All-Weather Monitoring: Unaffected by weather conditions, equipped with lightning protection facilities for long-term all-weather observation, suitable for flood control, geological disasters, and other fields.
- High Precision Monitoring: GNSS provides high-precision relative positioning, with practical deformation monitoring accuracy reaching ±(0.5-2)mm.
- High Stability: Average fault-free time exceeds 30,000 hours, with high protection level and anti-interference capability.
- Integrated with Cloud: Automatically connects to the platform for remote control, batch upgrades, and online maintenance, improving operational efficiency.
- Intelligent Integration: Built-in sensors achieve multi-mode intelligent switching, supporting various external sensors to meet different monitoring needs.
5.Summary
Ericco not only provides inertial sensors but also offers high-precision GNSS products, such as the ER-GNSS-C01/02 GNSS chip with a hot start time of <1s and a cold start time of <29s; ER-GNSS-R03 receiver, achieving centimeter-level positioning, and supporting BDS, GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, QZSS, SBAS.
More Technical Questions
1. Small Size, Big Impact: GNSS Chips Aid in Monitoring Landslide
2. Choosing an Accelerometer - MEMS or Quartz Accelerometer
3. Driving Automotive Evolution: MEMS Accelerometers
4. Factors Affecting the Stability of Q-Flex Accelerometers
5. Structure Design of High Precision Quartz Flexible Accelerometer
6. Methods to Maintain the Long-Term Performance of Quartz Flexure Accelerometers
Products in Article